you are currently visiting our website in a browser that is not supporting our website.

Product categories
Applications and innovations
Customer portal
Linde Gas Benelux - Buy Technical Gases, Pressure Regulators, and Accessories Online
Linde Gas – Your Partner in Industrial Gases
At Linde Gas, we build on more than 140 years of technological innovation. Thanks to the pioneering spirit of Carl von Linde, who invented the air separation plant in 1902, we have grown into the leading gas supplier in Europe. Today, we deliver high-quality gases in cylinders, tanks, and through pipelines, as well as on-site installations. Linde Gas is committed to innovation, quality, and reliability to meet our customers' diverse needs.
Optimized Industrial Gases from Linde Gas Benelux
Industrial gases play a crucial role in modern production processes and are essential for numerous applications. At Linde Gas Benelux, we offer a wide range of gases, including oxygen, nitrogen, argon, carbon dioxide, helium, acetylene, propane, and hydrogen. Our technical gases are indispensable in sectors such as the food industry, chemical industry, metallurgical processes, manufacturing industry, and research & development. By focusing on innovation, we deliver gases of the highest purity and quality, tailored to the strict requirements of specific applications, including medical or food-grade gases.
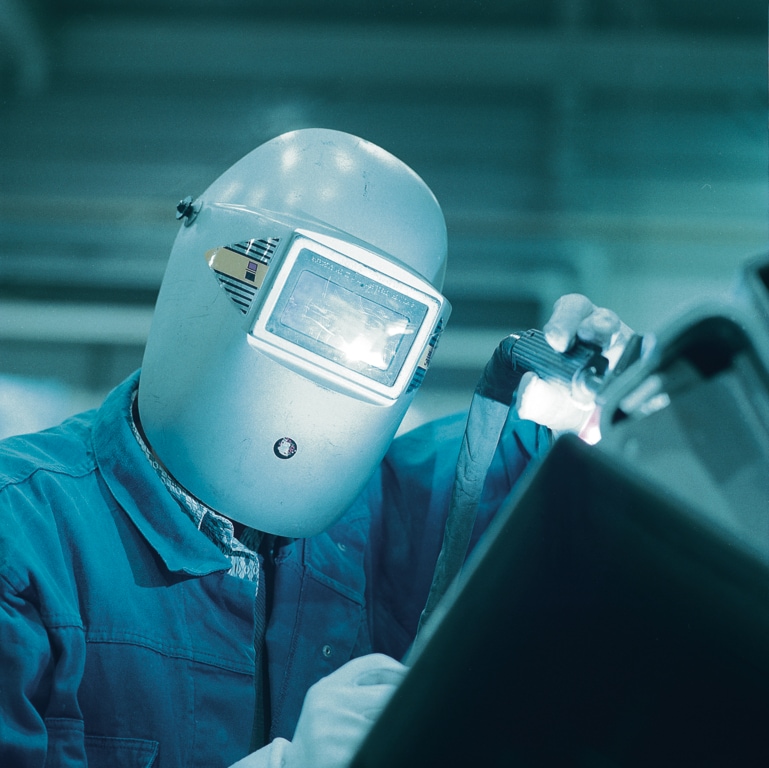
Welding and Cutting Gases – The Right Choice for Every Welding Process
At Linde Gas, we understand that each welding process has specific gas requirements. In our online webshop, you will find an extensive range of welding and cutting gases suitable for various techniques such as MIG/MAG welding and TIG welding. For arc welding processes, we offer shielding gases such as argon, helium, and advanced gas mixtures. Our welding and cutting gases, including MISON®, Heligon, Protegon and Protinox-S, meet the highest quality standards and are ideal for various applications such as thermal cutting, laser cutting, and plasma cutting.
Gases for the Food Industry
The food industry places high demands on food-grade gases. At Linde Gas Benelux, we supply top-quality gases that fully comply with legal requirements. Our range includes products such as BANARG®, Foodmix, and Foodgrade, specially developed for food packaging and protection during storage. With our offering of high-quality food-grade gases, we support the food industry in maintaining product quality, freshness, and safety.
Gas Accessories for Safe and Efficient Operations
In addition to our wide range of gases, Linde Gas Benelux also offers high-quality gas equipment and accessories. In our online customer portal, you will find pressure regulators, gas analyzers, preheaters, gas detection, cryogenic hardware, cylinder trolleys, and more. Explore our extensive selection of tools and accessories in the Linde Gas Benelux webshop.